This article is an attempt to make a nice guide or a cheat sheet for some common types of plots from basic to advanced level. For doing all the exercises here, I used RStudio. Hopefully, that’s good for you as well. Let’s start with the basics. This is the command to install the ggplot2 if you do not have it already: install.packages('ggplot2'). Cheat Sheet of graphics, the ggplot2 is based on the grammar idea that you can build every graph from the same Basics components: a data set, a coordinate. Base R Graphics Cheat Sheet David Gerard August 8, 2017. Abstract: I reproduce some of the plots from Rstudio’s ggplot2 cheat sheet using Base R graphics.
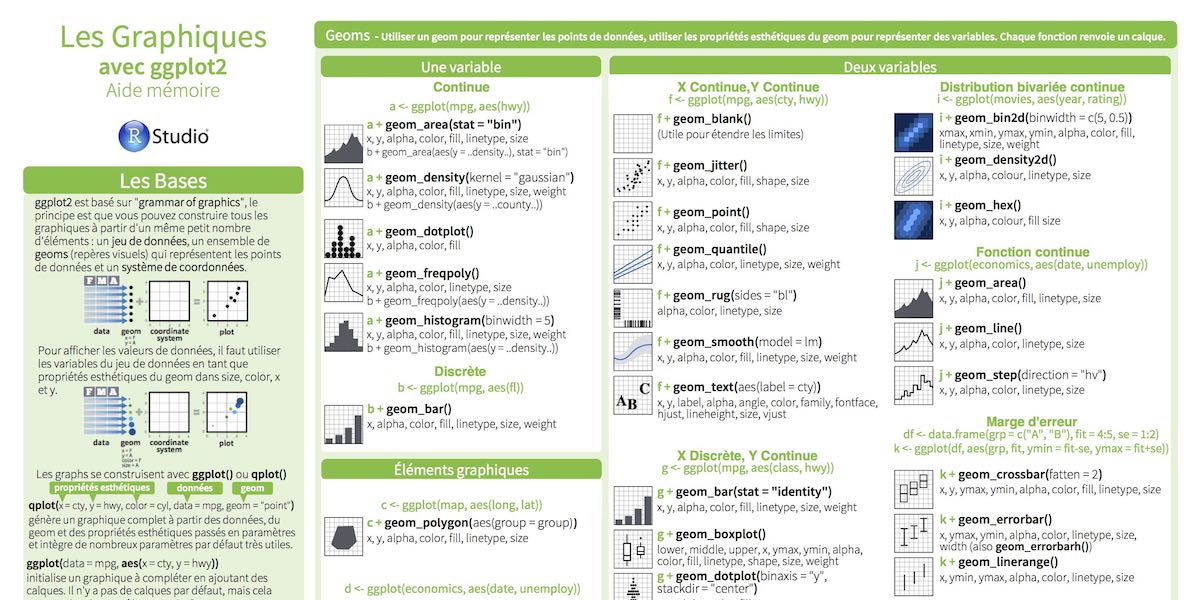
- Cheat Sheet RStudio® is a trademark of RStudio, Inc. CC BY RStudio. info@rstudio.com. 844-448-1212. rstudio.com Learn more at docs.ggplot2.org. ggplot2 0.9.3.1. Updated: 3/15 Geoms- Use a geom to represent data points, use the geom’s aesthetic properties to represent variables. Each function returns a.
- The cheat sheet article includes downloadable ggplot2 RStudio code snippets, offering ready-to-use, fill-in-the-placeholder code for a variety of ggplot2 tasks.
5.1 Plotting with ggplot2
ggplot2 is a plotting package that makes it simple to create complex plots from data in a data frame. Driver for canon lide 110 for mac. It provides a more programmatic interface for specifying what variables to plot, how they are displayed, and general visual properties. Therefore, we only need minimal changes if the underlying data change or if we decide to change from a bar plot to a scatter plot. This helps in creating publication quality plots with minimal amounts of adjustments and tweaking.
R-studio Cheats
ggplot2 functions like data in the ‘long’ format, i.e., a column for every dimension, and a row for every observation. Well-structured data will save you lots of time when making figures with ggplot2
Rstudio Ggplot2 Cheat Sheet Pdf
ggplot graphics are built step by step by adding new elements. Adding layers in this fashion allows for extensive flexibility and customization of plots.
To build a ggplot, we will use the following basic template that can be used for different types of plots:
- use the
ggplot()function and bind the plot to a specific data frame using thedataargument
- define a mapping (using the aesthetic (
aes) function), by selecting the variables to be plotted and specifying how to present them in the graph, e.g. as x/y positions or characteristics such as size, shape, color, etc.
add ‘geoms’ – graphical representations of the data in the plot (points, lines, bars).
ggplot2offers many different geoms; we will use some common ones today, including:geom_point()for scatter plots, dot plots, etc.geom_boxplot()for, well, boxplots!geom_line()for trend lines, time series, etc.
Rstudio Ggplot2 Cheat Sheet

Rstudio Ggplot2 Cheat Sheet 2017
To add a geom to the plot use the + operator. Free cubase software download. Because we have two continuous variables, let’s use geom_point() first:
The + in the ggplot2 package is particularly useful because it allows you to modify existing ggplot objects. This means you can easily set up plot templates and conveniently explore different types of plots, so the above plot can also be generated with code like this:

Notes
Ggplot2 Cheat Sheet R
- Anything you put in the
ggplot()function can be seen by any geom layers that you add (i.e., these are universal plot settings). This includes the x- and y-axis mapping you set up inaes(). - You can also specify mappings for a given geom independently of the mappings defined globally in the
ggplot()function. - The
+sign used to add new layers must be placed at the end of the line containing the previous layer. If, instead, the+sign is added at the beginning of the line containing the new layer,ggplot2will not add the new layer and will return an error message.
